Aug 10, 2020. Article. Dozens of times over the last decade NASA scientists have launched laser beams at a reflector the size of a paperback novel about 240,000 miles (385,000 kilometers) away from Earth. They announced today, in collaboration with their French colleagues, that they received signal back for the first time, an encouraging result.. To time how long it takes a pulse of laser light to travel from space to Earth and back, you need a really good stopwatch — one that can measure within a fraction of a billionth of a second. That kind of timer is exactly what engineers have built at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, for the Ice, Cloud and land.
How Far Can a Laser Beam Travel? Exploring the Maximum Range of Laser Technology The

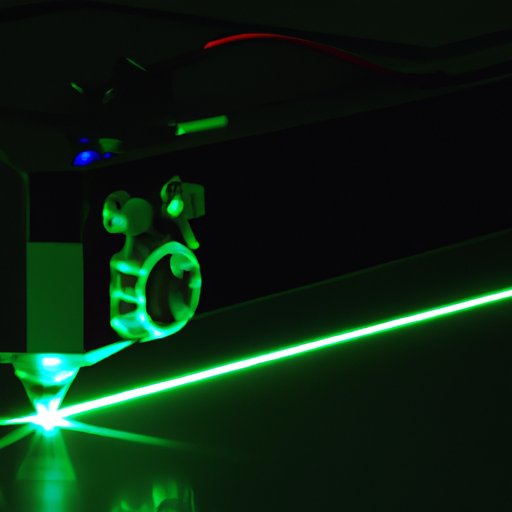
Laser beams are focused by a lens. Smithsonian Photo Contest Smithsonian Magazine

What Is a Laser? How Does It Work? Optics Mag

Refraction of Laser Beam FlatEarth.ws
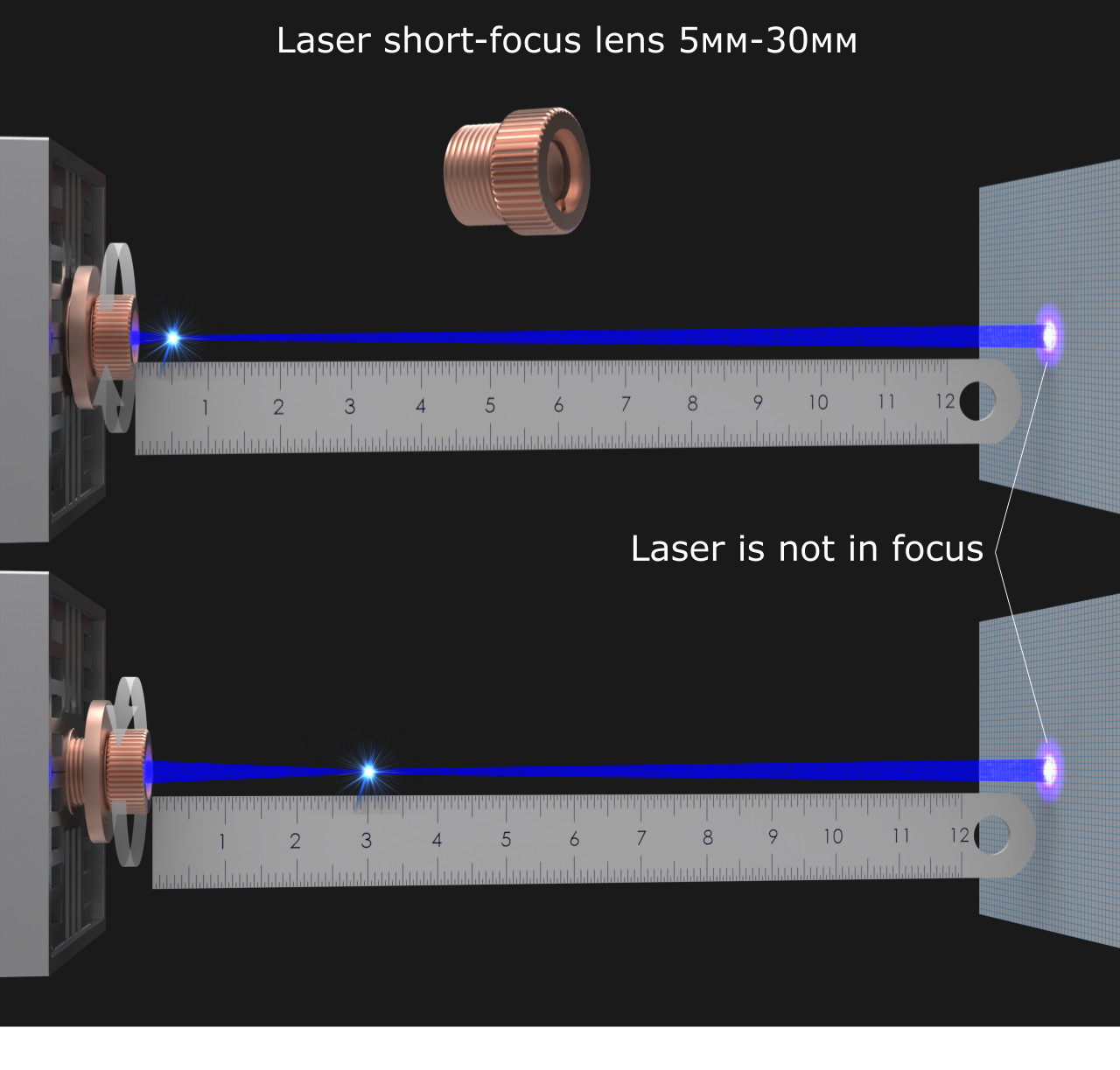
Laser beam focusing How to make Best laser focus!
.jpg)
The Different Types of Lasers and Lasing Media
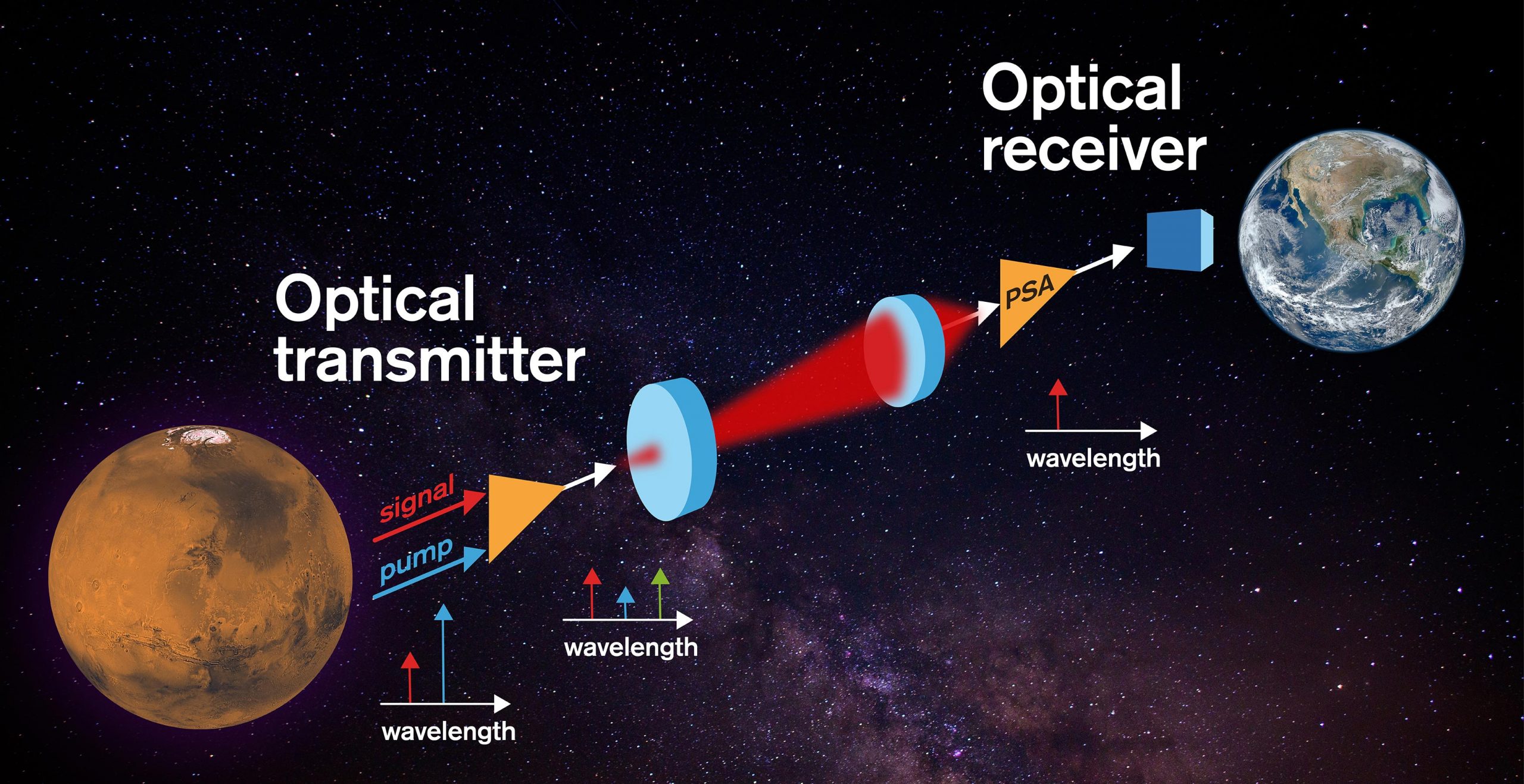
The Most Sensitive Optical Receivers Yet for for LaserBeam Based Space Communications
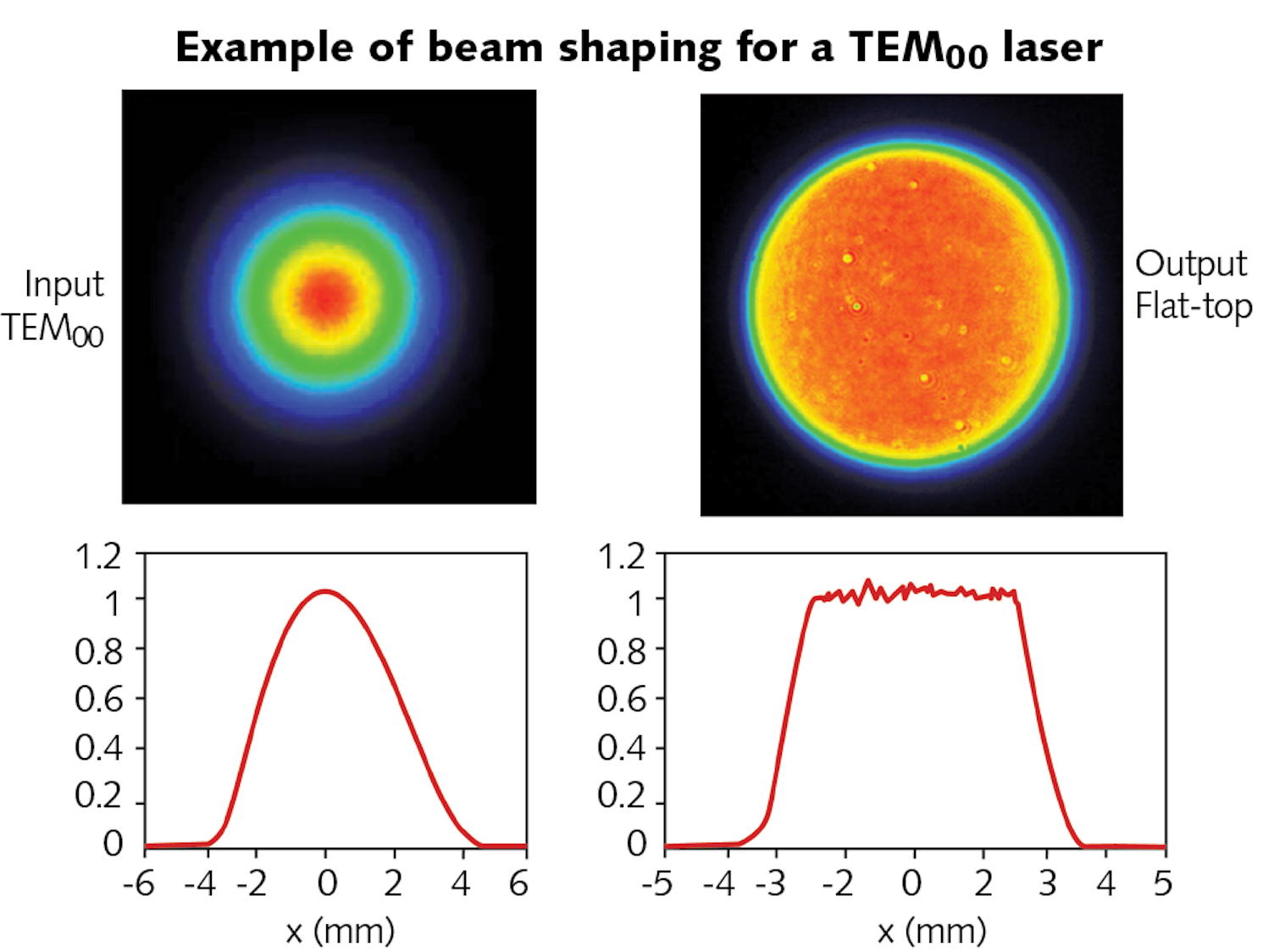
Flattop laser beams Their uses and benefits Laser Focus World

Laser Physics Basics American Laser Study Club
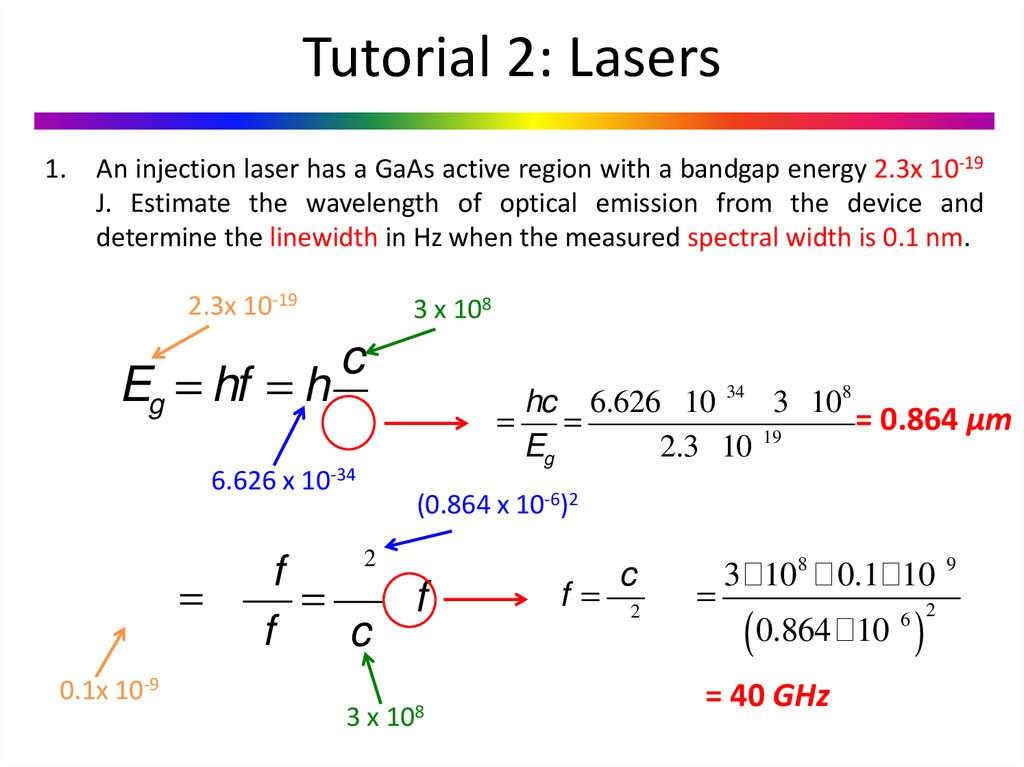
Lasers. Tutorial 2 online presentation
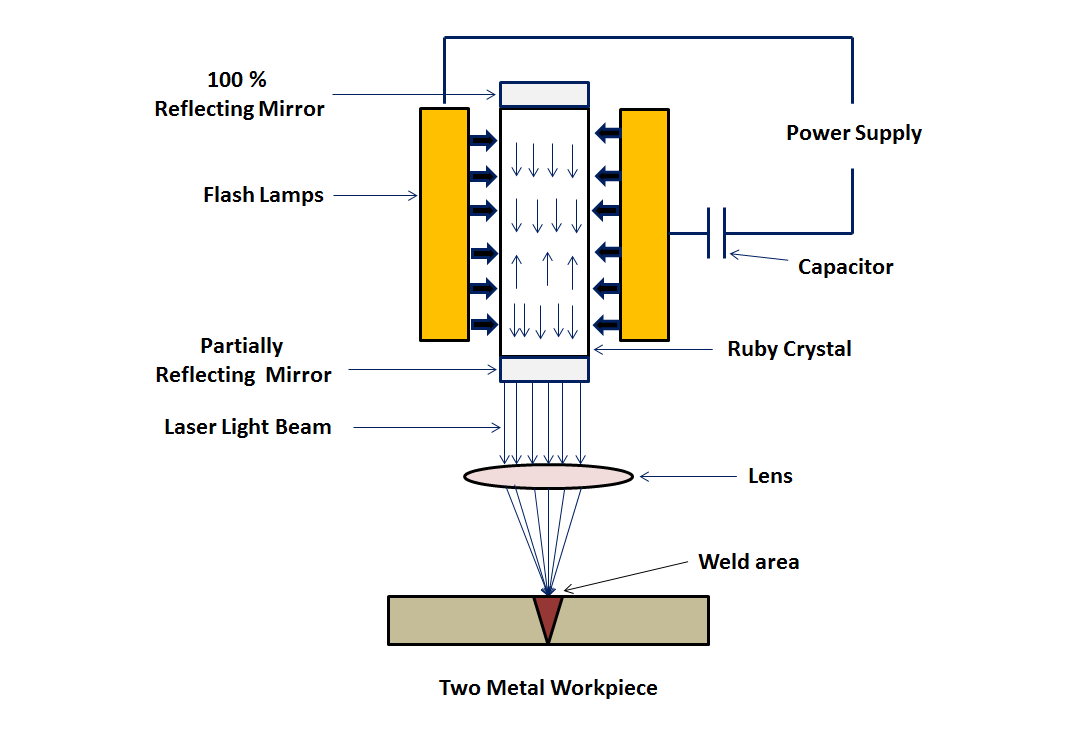
les types de lasers pdf
Laser Beam Sound Board The Best Picture Of Beam

How to Align an Invisible Laser Beam YouTube

Lasers Beams The Best Picture Of Beam
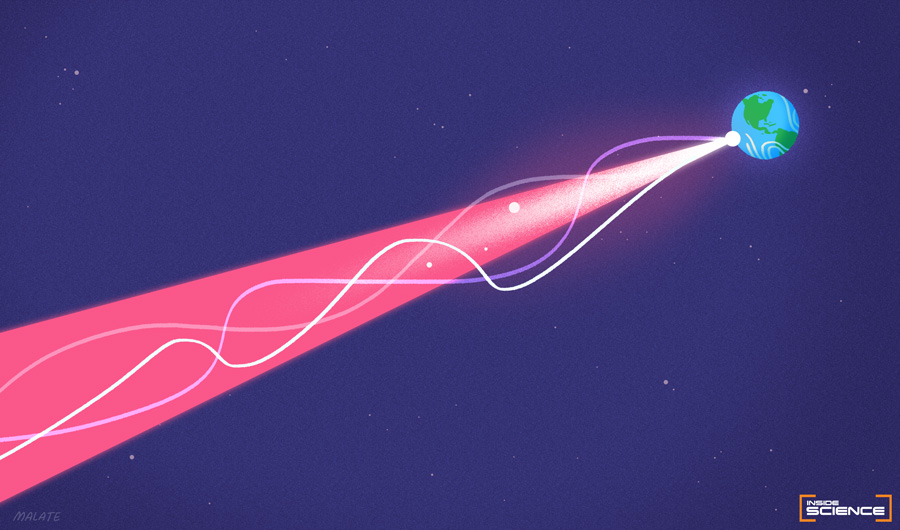

How Far Can Laser Light Travel? Inside Science
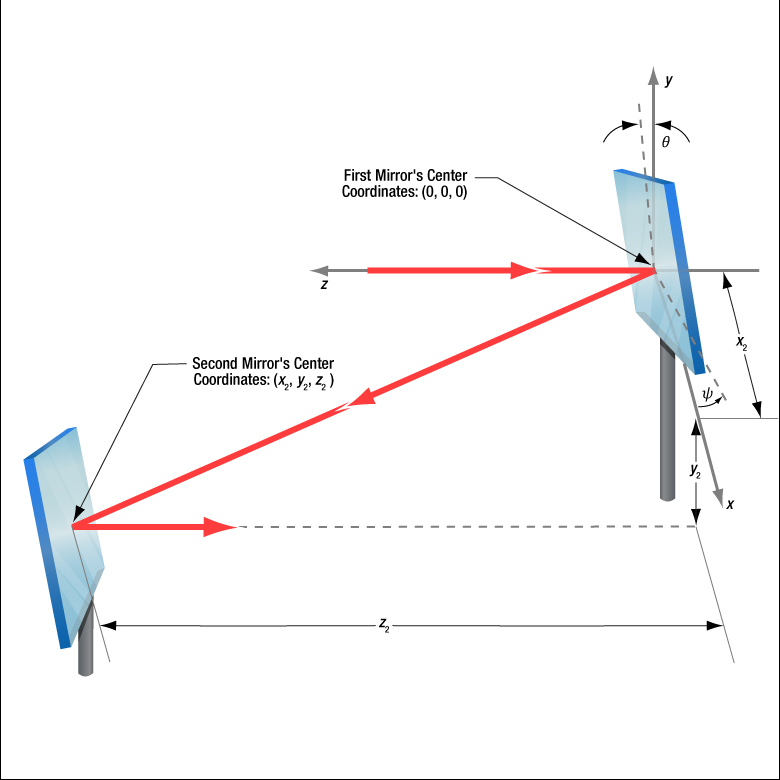
How To Reflect A Laser Beam With Mirrors The Best Picture Of Beam

Visible Laser Beam Wavelength The Best Picture Of Beam
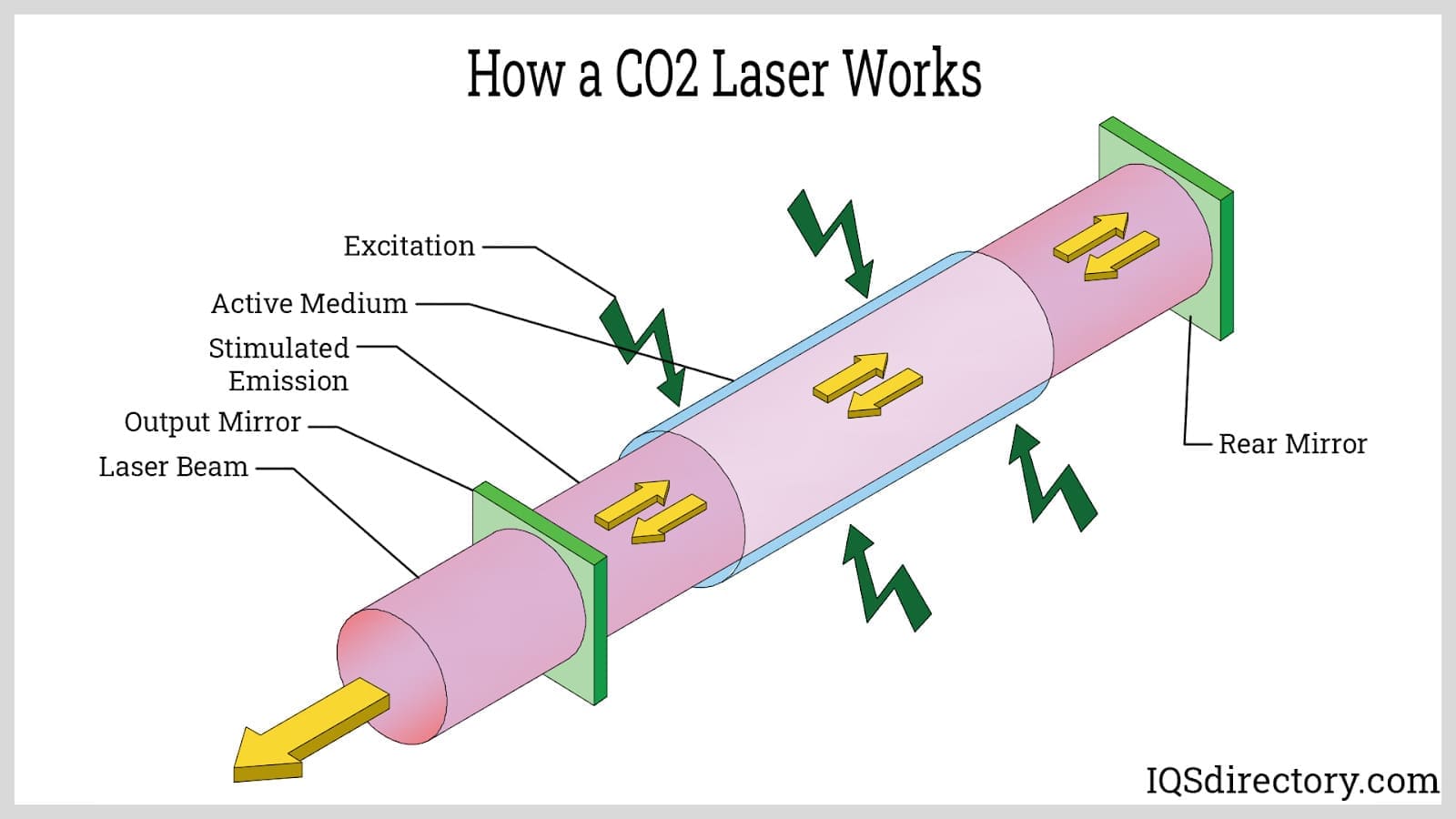
Co2 Laser Beam Delivery System The Best Picture Of Beam
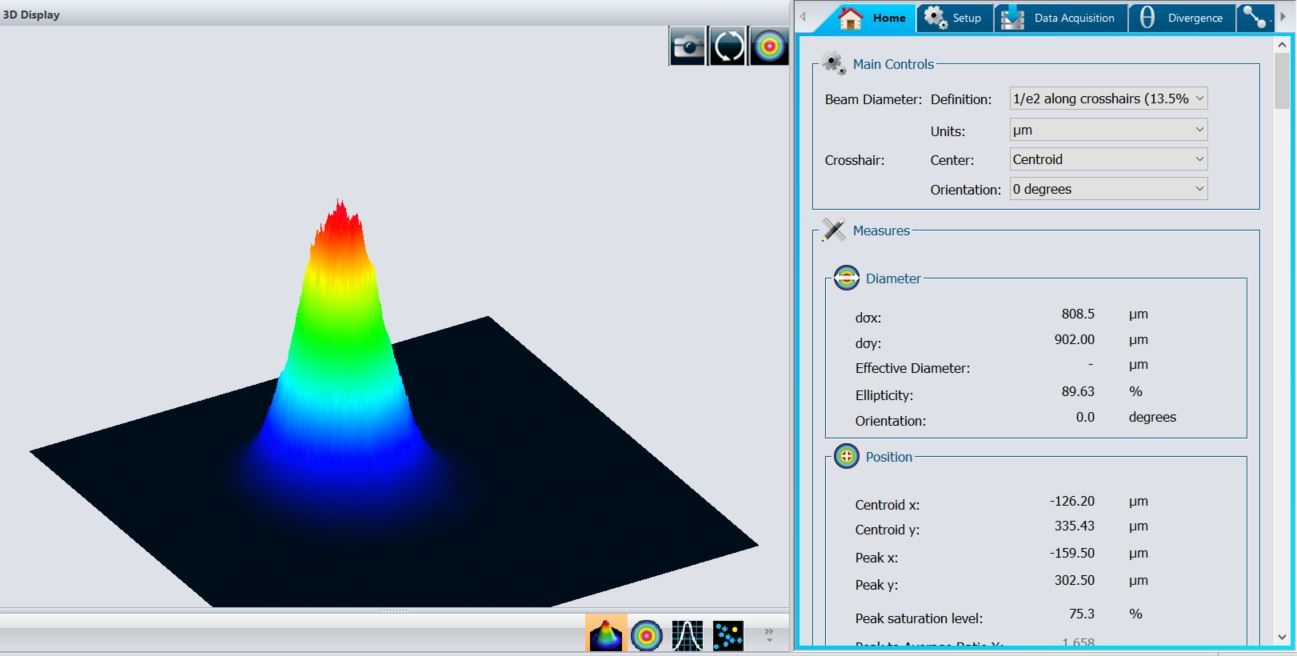
The beginner's guide on spot size of laser beam

Laser Physics Basics American Laser Study Club
It calls for a ground-based laser array on the order of 0.4 square miles (1 square kilometer) and as powerful as 100 gigawatts, which would be by far the most powerful laser ever made on Earth.. The ED 50 distance is 0.316 times the NOHD (a little less than 1/3 the NOHD distance). At the ED 50 distance, there is roughly a 50-50 chance that a fixed laser beam aimed into an unmoving eye under laboratory conditions will cause the smallest medically detectable change to the retina. Such small changes can heal — just as small skin cuts and burns can heal with no adverse effect.